Understanding the average height in the US for women is more than just a statistical curiosity. It delves into cultural norms, health trends, and biological factors that influence physical development. In recent years, this topic has gained attention due to its implications on societal standards and health assessments.
The concept of average height is not merely a number but a reflection of various factors, including genetics, nutrition, and lifestyle. For women in the United States, these factors have shaped their physical growth over the decades. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the average height in the US for women, shedding light on its significance and implications.
Whether you're a researcher, a health enthusiast, or simply curious about human development, this article will offer valuable insights into the topic. By examining the data and understanding the contributing factors, we can gain a deeper appreciation of the diversity in human height and its broader implications.
Read also:Monsters Inc Salamander Unveiling The Fascinating World Of Amphibian Stars
Daftar Isi
Biological Factors Influencing Height
Nutrition and Its Impact on Height
Historical Perspective on Women's Height
Current Statistics on Average Height
Read also:Why Is Missouri Called A Spelunkers Paradise
Regional Differences in Height
Societal Standards and Height Perception
Future Trends in Height Development
Biological Factors Influencing Height
Height is primarily determined by a combination of biological factors. Hormones such as growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) play crucial roles in the development of height during childhood and adolescence. For women in the US, the interplay between these hormones and genetic predispositions significantly impacts their final adult height.
Key Biological Factors:
- Growth Hormone Regulation
- Thyroid Function
- Sex Hormones (Estrogen)
Additionally, the timing of puberty can influence height outcomes. Early or late onset of puberty can affect the duration of growth spurts, thereby impacting final height. Understanding these biological processes provides a foundation for analyzing height variations among women.
Nutrition and Its Impact on Height
Nutrition is a critical determinant of height, especially during formative years. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients such as protein, calcium, vitamin D, and iron supports optimal bone growth and development. Studies have shown that inadequate nutrition during childhood can lead to stunted growth and lower average height in adulthood.
Nutrient-Rich Foods for Height Growth:
- Dairy Products
- Lean Proteins
- Fruits and Vegetables
- Whole Grains
Moreover, access to proper nutrition varies across socioeconomic groups, contributing to disparities in average height among women in different regions of the US.
The Role of Genetic Heritage
Genetics accounts for approximately 60-80% of height variability. Women inherit height-related genes from both parents, which interact with environmental factors to determine their final height. Research indicates that specific gene variants, such as those found in the HMGA2 gene, are strongly associated with height differences.
Key Genetic Factors:
- Parental Height
- Gene Variants
- Epigenetic Modifications
While genetics sets the potential for height, environmental factors like nutrition and health care can either enhance or limit this potential. This interplay highlights the complexity of height determination.
Historical Perspective on Women's Height
Over the past century, the average height of women in the US has seen gradual increases. Improved living conditions, better healthcare, and advancements in nutrition have contributed to this trend. For instance, data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) shows that the average height for women increased from 63.7 inches in the early 1960s to approximately 63.9 inches in recent years.
Historical Data on Women's Height:
- 1960s: 63.7 inches
- 1980s: 64 inches
- 2020s: 63.9 inches
Despite these improvements, the rate of increase has slowed in recent decades, suggesting a plateau in height growth for women in the US.
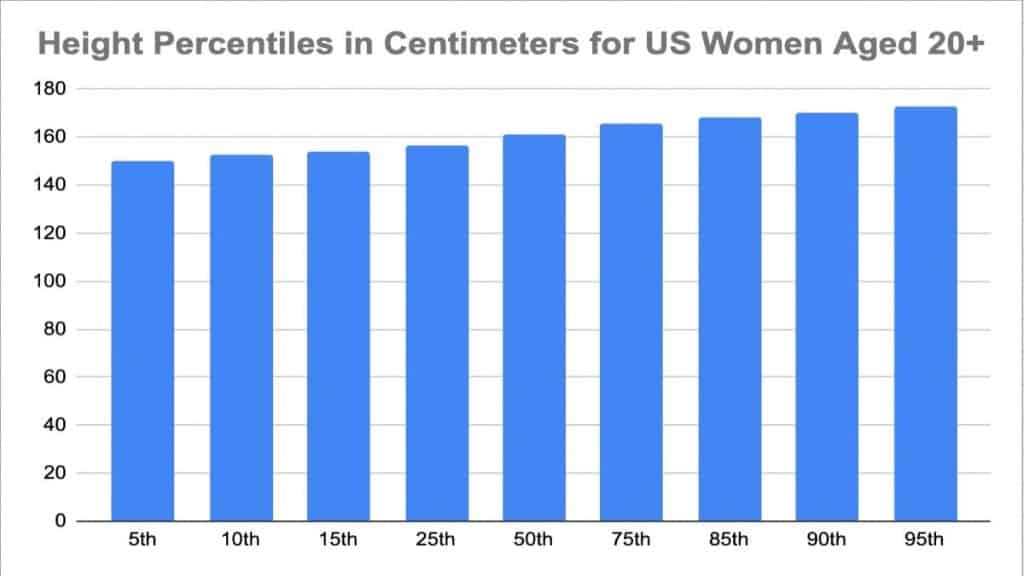
Current Statistics on Average Height
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the average height for women in the US is approximately 63.9 inches (5 feet 3.9 inches). This statistic is based on a comprehensive survey of adult women aged 20 and above. It is important to note that these figures represent a national average and may vary across different demographic groups.
Key Statistics:
- Average Height: 63.9 inches
- Age Range: 20 years and above
- Sample Size: Over 5,000 participants
These statistics provide a baseline for understanding height trends and comparing them with other countries or regions.
Regional Differences in Height
Regional variations in height exist within the US due to differences in genetics, lifestyle, and access to resources. Women from the Northeast, for example, tend to be slightly taller than those from the South, possibly due to variations in dietary habits and socioeconomic factors.
Regional Height Comparisons:
- Northeast: Average 64.2 inches
- South: Average 63.6 inches
- West: Average 63.9 inches
These differences underscore the importance of considering regional contexts when analyzing height data.
Health Implications of Height
Height is not only a physical attribute but also a health indicator. Women of shorter stature may face an increased risk of certain health conditions, such as osteoporosis and cardiovascular diseases. Conversely, taller women may have a higher risk of certain cancers, including breast and ovarian cancer.
Health Risks Associated with Height:
- Shorter Height: Osteoporosis, Cardiovascular Diseases
- Taller Height: Certain Cancers, Joint Issues
Understanding these health implications can inform personalized healthcare strategies and preventive measures.
Societal Standards and Height Perception
Societal standards regarding height often influence perceptions of beauty and success. In many cultures, including the US, taller women are sometimes perceived as more confident and capable. However, these standards can create unrealistic expectations and contribute to body image issues.
Societal Expectations:
- Media Representation
- Cultural Norms
- Workplace Bias
Challenging these norms and promoting body positivity can help reduce the negative impact of societal height standards.
Future Trends in Height Development
Looking ahead, advancements in genetics, nutrition, and healthcare may further influence height trends. As personalized medicine becomes more prevalent, interventions tailored to individual genetic profiles could optimize height potential. Additionally, addressing global health disparities can ensure equitable access to resources that support optimal growth.
Potential Future Developments:
- Genetic Engineering
- Targeted Nutrition Programs
- Improved Healthcare Access
These developments hold promise for enhancing overall well-being and promoting diversity in human height.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the average height in the US for women is shaped by a complex interplay of biological, genetic, and environmental factors. Understanding these influences not only provides insights into physical development but also highlights the broader implications for health and society. By examining the data and addressing disparities, we can work towards a future where height becomes a reflection of health and well-being rather than societal expectations.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more in-depth insights into related topics. Together, let's continue the conversation and promote a deeper understanding of human development and diversity.