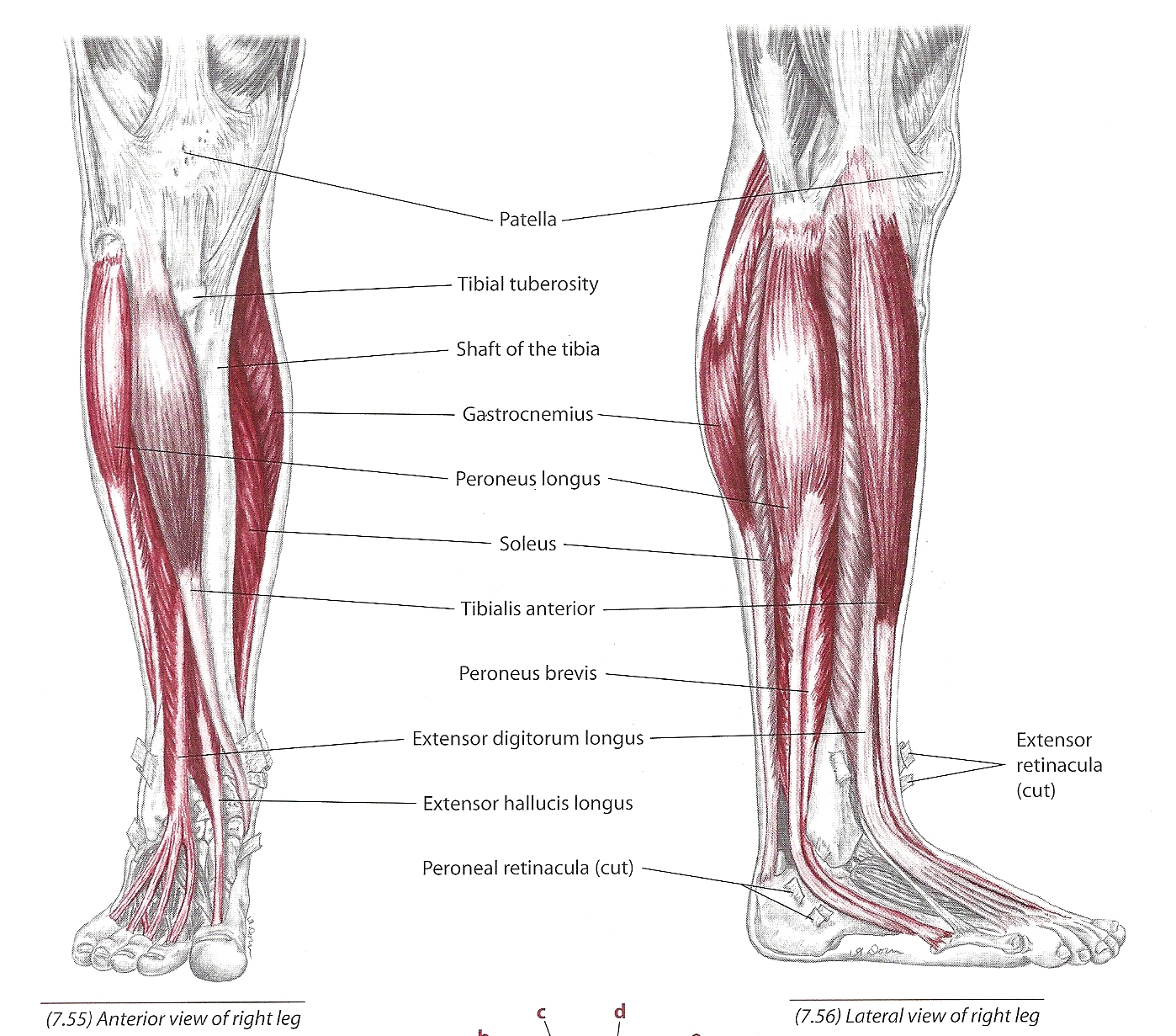
The tibialis anterior muscle plays a crucial role in our daily activities, from walking to running. Understanding this muscle's anatomy, function, and potential issues can help maintain overall leg health. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast or someone dealing with leg pain, this guide provides valuable insights into the tibialis anterior muscle.
Have you ever wondered what makes walking, running, or even standing possible? The tibialis anterior muscle is one of the key muscles responsible for these activities. Located in the front of the lower leg, it is essential for ankle movement and maintaining balance. Injuries or conditions affecting this muscle can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
Throughout this article, we will explore the anatomy, function, and importance of the tibialis anterior muscle. We'll also delve into common injuries, treatment options, and exercises to strengthen this vital muscle. By the end of this guide, you'll have a better understanding of how to care for your tibialis anterior muscle and prevent potential issues.
Read also:Top Patreon Alternatives For Creators Building A Thriving Community
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Function of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Common Injuries to the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Diagnosis of Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries
- Treatment Options for Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries
- Exercises to Strengthen the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Preventing Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries
- Nutrition and Supplements for Muscle Health
- Rehabilitation Techniques for Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The tibialis anterior muscle is one of the primary muscles in the lower leg. It originates from the upper two-thirds of the lateral surface of the tibia bone and inserts into the medial cuneiform and the base of the first metatarsal bone. This muscle is surrounded by the deep fascia of the leg, which helps stabilize it during movement.
Location and Structure
This muscle is located in the anterior compartment of the leg and is the largest muscle in this region. Its primary structure consists of long, thin fibers that run parallel to the tibia. The tibialis anterior muscle is innervated by the deep fibular nerve (L4-L5), which supplies the necessary motor control for its function.
According to a study published in the National Library of Medicine, the tibialis anterior muscle plays a significant role in the biomechanics of the lower limb. Its unique position and structure make it essential for various movements, including dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot.
Function of the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The primary function of the tibialis anterior muscle is to facilitate dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot. Dorsiflexion refers to the movement that pulls the foot upwards, while inversion involves tilting the sole of the foot inward. These movements are critical for walking, running, and maintaining balance.
Role in Daily Activities
- Walking: The tibialis anterior muscle helps lift the foot during the swing phase of walking.
- Running: It stabilizes the ankle joint during high-impact activities like running.
- Balance: This muscle works in conjunction with other muscles to maintain stability while standing or walking on uneven surfaces.
A well-functioning tibialis anterior muscle ensures smooth and efficient movement, reducing the risk of injury during physical activities.
Common Injuries to the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Despite its importance, the tibialis anterior muscle is prone to various injuries, particularly in athletes and individuals with repetitive strain. Common injuries include shin splints, tendonitis, and muscle strains.
Read also:Kylie Jenners Dad The Story Behind The Fame
Shin Splints
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, occur when the tibialis anterior muscle becomes overworked. Symptoms include pain along the shin bone, swelling, and tenderness. This condition is common in runners and individuals who engage in high-impact activities.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis of the tibialis anterior muscle involves inflammation of the tendon. This condition is often caused by repetitive motion or overuse. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and difficulty in dorsiflexion.
Diagnosis of Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries
Diagnosing tibialis anterior muscle injuries involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and patient history. A healthcare professional will assess the range of motion, strength, and any signs of inflammation or swelling.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays: Used to rule out fractures or other bone-related issues.
- Ultrasound: Helps visualize soft tissue injuries, such as tendon tears or inflammation.
- MRI: Provides detailed images of muscle and tendon structures, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing long-term complications and ensuring proper healing.
Treatment Options for Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries
Treatment for tibialis anterior muscle injuries depends on the severity and type of injury. Options range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to surgical intervention in severe cases.
Conservative Treatment
- Rest: Allowing the muscle to heal by avoiding activities that exacerbate the injury.
- Ice: Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and pain.
- Compression: Using compression bandages to support the muscle and reduce swelling.
- Elevation: Elevating the leg to minimize swelling.
In addition to these measures, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications may be recommended to manage pain and inflammation.
Exercises to Strengthen the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Strengthening the tibialis anterior muscle is essential for preventing injuries and improving overall leg health. Here are some effective exercises:
Resistance Band Dorsiflexion
Attach a resistance band to a stable object and loop it around the top of your foot. Pull your foot upward against the resistance, holding for a few seconds before releasing. Repeat 10-15 times for 2-3 sets.
Toe Raises
Stand with your feet flat on the ground. Slowly lift your heels off the ground, balancing on your toes. Hold for a few seconds, then lower your heels back down. Perform 10-15 repetitions for 2-3 sets.
Preventing Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries
Preventing injuries to the tibialis anterior muscle involves adopting healthy habits and proper techniques during physical activities. Here are some tips:
Proper Footwear
Wearing well-fitted shoes with adequate support can reduce the strain on the tibialis anterior muscle. Choose shoes specifically designed for your activity level and foot type.
Gradual Progression
When starting a new exercise routine or increasing intensity, do so gradually to allow your muscles to adapt. Sudden changes can lead to overuse injuries.
Nutrition and Supplements for Muscle Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in maintaining muscle health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals can support the tibialis anterior muscle's function and recovery.
Key Nutrients
- Protein: Essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Vitamin D: Promotes bone health and supports muscle function.
- Magnesium: Helps regulate muscle contractions and nerve function.
Supplements like omega-3 fatty acids and creatine may also benefit muscle health, but consult a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen.
Rehabilitation Techniques for Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Rehabilitation is crucial for restoring function and strength after an injury. A comprehensive rehabilitation program includes physical therapy, targeted exercises, and lifestyle modifications.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design a personalized rehabilitation plan focusing on flexibility, strength, and balance. Techniques such as massage, ultrasound therapy, and electrical stimulation may also be used to enhance recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Tibialis Anterior Muscle
What Causes Pain in the Tibialis Anterior Muscle?
Pain in the tibialis anterior muscle is often caused by overuse, repetitive strain, or sudden increases in physical activity. Conditions like shin splints and tendonitis are common culprits.
How Long Does It Take to Recover from a Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injury?
Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury. Mild strains may heal within a few weeks, while more severe injuries could take several months. Following a proper rehabilitation program can speed up recovery.
Can Stretching Prevent Tibialis Anterior Muscle Injuries?
Yes, regular stretching can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury. Focus on exercises that target the tibialis anterior muscle and surrounding areas for optimal results.
Kesimpulan
The tibialis anterior muscle is a vital component of lower leg anatomy, playing a crucial role in movement and balance. Understanding its function, potential injuries, and preventive measures can help maintain overall leg health. By incorporating strengthening exercises, proper nutrition, and rehabilitation techniques, you can ensure the longevity and efficiency of this essential muscle.
Take action today by implementing the tips and exercises outlined in this guide. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below, and don't forget to explore other informative articles on our website. Together, let's prioritize our muscle health and lead active, fulfilling lives!