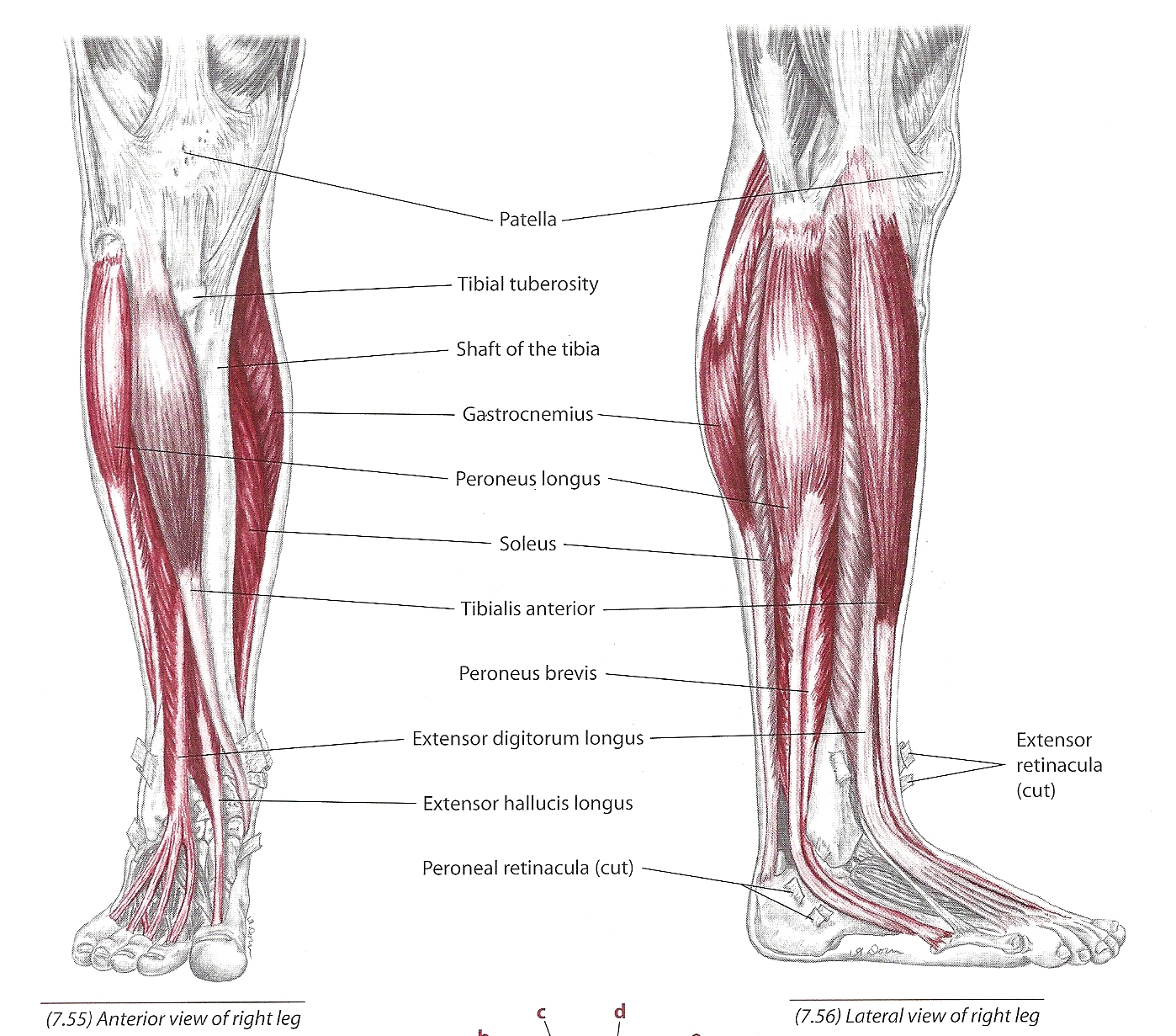
The tibialis anterior muscle is one of the most important muscles in the lower leg that plays a crucial role in movement and stability. It is essential for everyday activities such as walking, running, and maintaining balance. This muscle helps control the movement of the foot and ankle, making it a vital component of lower leg anatomy.
Many people overlook the importance of the tibialis anterior muscle until they experience pain or discomfort in the lower leg. Understanding its function and anatomy can help you identify potential issues and take preventive measures to avoid injuries. In this article, we will delve into the function, anatomy, and significance of the tibialis anterior muscle.
Whether you are a fitness enthusiast, an athlete, or someone looking to improve your overall health, this article will provide valuable insights into the tibialis anterior muscle. By the end of this piece, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how this muscle works and its impact on your daily life.
Read also:Monsters Inc Salamander Unveiling The Fascinating World Of Amphibian Stars
Table of Contents
- Tibialis Anterior Muscle Anatomy
- Function of Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Biomechanics and Movement Patterns
- Common Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Preventing Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Strengthening Exercises for Tibialis Anterior
- Stretching Techniques for Tibialis Anterior
- Nutrition and Muscle Health
- Summary and Key Takeaways
Tibialis Anterior Muscle Anatomy
The tibialis anterior muscle is located in the front of the lower leg and is part of the anterior compartment. It originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. This muscle is surrounded by the deep fascia of the leg and is innervated by the deep fibular nerve.
Understanding the anatomy of the tibialis anterior muscle is essential for recognizing its role in movement and stability. It works in conjunction with other muscles in the lower leg to facilitate smooth and coordinated motion.
Key Anatomical Features
- Origin: Lateral condyle of the tibia
- Insertion: Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones
- Innervation: Deep fibular nerve
- Function: Dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot
Function of Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The primary function of the tibialis anterior muscle is dorsiflexion of the foot, which is the movement that pulls the toes toward the shin. Additionally, it assists in foot inversion, which is the movement that turns the sole of the foot inward. These actions are critical for maintaining balance and ensuring proper gait mechanics.
Research has shown that the tibialis anterior muscle plays a significant role in shock absorption during walking and running. Its ability to control the descent of the foot during the swing phase of gait helps protect the joints and soft tissues from excessive stress.
Biomechanics and Movement Patterns
The biomechanics of the tibialis anterior muscle involve a complex interaction with other muscles and structures in the lower leg. During the gait cycle, this muscle activates to lift the foot off the ground and prepare it for the next step. This action is particularly important during activities that require rapid changes in direction, such as sports or dancing.
Key Biomechanical Roles
- Dorsiflexion during the swing phase of gait
- Foot stabilization during weight-bearing activities
- Coordination with other muscles in the lower leg
Common Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Tibialis anterior injuries are relatively common, especially among athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive activities involving the lower leg. Some of the most frequent injuries include shin splints, tendonitis, and muscle strains. These conditions can result from overuse, improper technique, or insufficient rest and recovery.
Read also:Best Foundation For Combination Skin A Comprehensive Guide To Flawless Complexion
According to a study published in the Journal of Sports Medicine, shin splints are one of the leading causes of lower leg pain in runners. The study highlights the importance of addressing muscle imbalances and improving flexibility to reduce the risk of injury.
Preventing Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Preventing tibialis anterior injuries involves a combination of proper training techniques, adequate rest, and targeted exercises. Incorporating strength and flexibility routines into your workout regimen can help maintain muscle health and reduce the likelihood of injury.
Tips for Injury Prevention
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of workouts
- Use proper footwear with adequate support
- Incorporate rest days into your training schedule
Rehabilitation and Recovery
In the event of a tibialis anterior injury, rehabilitation is essential for restoring muscle function and preventing future complications. A comprehensive rehabilitation program typically includes exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and balance. Working with a physical therapist can help tailor the program to your specific needs and goals.
A study published in the Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy found that eccentric training exercises are particularly effective in promoting recovery from tibialis anterior injuries. These exercises focus on controlled muscle lengthening, which enhances muscle strength and endurance.
Strengthening Exercises for Tibialis Anterior
Strengthening the tibialis anterior muscle is crucial for improving performance and preventing injuries. There are several exercises that target this muscle group, ranging from simple at-home routines to more advanced gym workouts.
Effective Strengthening Exercises
- Resistance band dorsiflexion
- Toe raises on a step
- Calf raises with emphasis on dorsiflexion
Stretching Techniques for Tibialis Anterior
Stretching the tibialis anterior muscle is equally important for maintaining flexibility and reducing tension. Incorporating regular stretching routines into your daily schedule can help improve muscle function and enhance overall mobility.
Recommended Stretching Techniques
- Seated ankle dorsiflexion stretch
- Standing shin stretch
- Wall-assisted foot inversion stretch
Nutrition and Muscle Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle health and recovery. Consuming a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support the tibialis anterior muscle and other soft tissues in the lower leg. Key nutrients such as protein, vitamins, and minerals are crucial for muscle repair and growth.
A study published in the Journal of Nutrition emphasizes the importance of adequate protein intake for muscle maintenance. The study suggests that consuming high-quality protein sources, such as lean meats, fish, and plant-based alternatives, can optimize muscle health and recovery.
Summary and Key Takeaways
The tibialis anterior muscle is a critical component of lower leg anatomy, responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot. Its role in movement and stability makes it essential for everyday activities and athletic performance. Understanding its function, biomechanics, and potential injuries can help you take proactive steps to maintain muscle health.
To summarize:
- The tibialis anterior muscle facilitates dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot
- Common injuries include shin splints, tendonitis, and muscle strains
- Prevention involves proper training techniques and targeted exercises
- Rehabilitation focuses on strengthening, flexibility, and balance
- Nutrition supports muscle repair and growth
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into health and fitness. Together, let's promote a healthier and more active lifestyle!