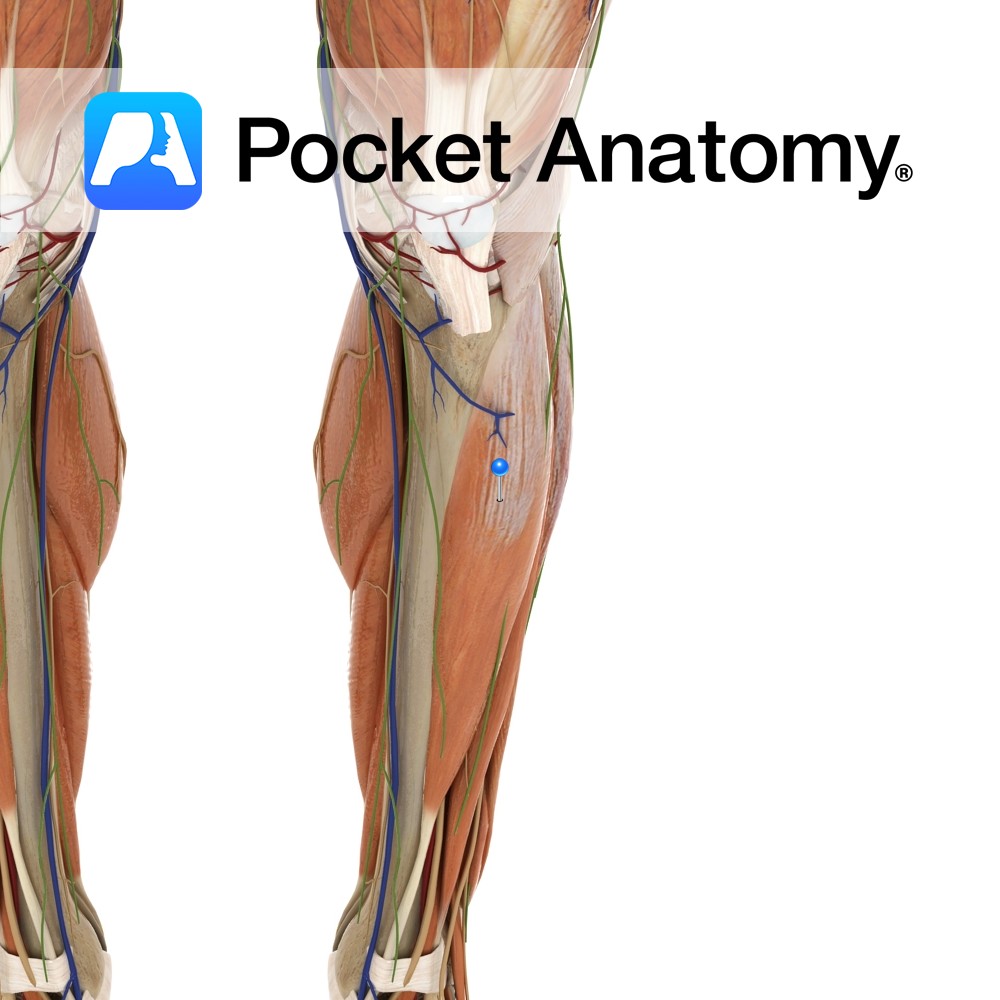
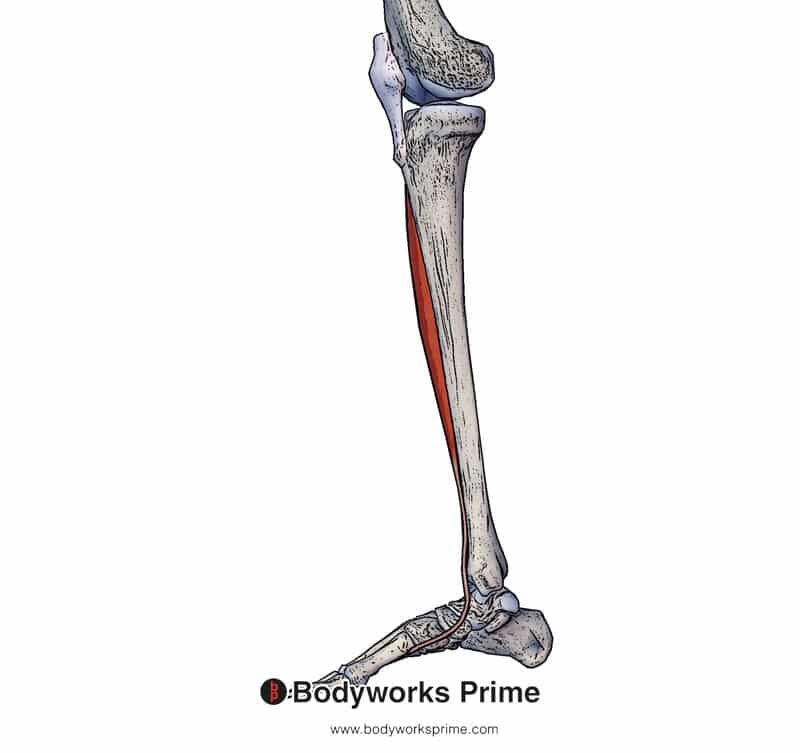
The tibialis anterior is a crucial muscle located in the front of the lower leg. It plays a significant role in foot movement, posture, and balance. Understanding its anatomy, functions, and potential disorders can help in maintaining overall leg health and preventing injuries. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, a healthcare professional, or simply someone curious about human anatomy, this article will provide comprehensive insights into the tibialis anterior muscle.
As one of the primary muscles involved in dorsiflexion, the tibialis anterior is essential for walking, running, and various other physical activities. Injuries or disorders affecting this muscle can significantly impact mobility and quality of life. By gaining a deeper understanding of its structure and role, we can better appreciate the importance of taking care of our muscles.
This article delves into the anatomy, function, and common conditions associated with the tibialis anterior. Additionally, it provides practical tips for maintaining muscle health and preventing injuries. With the information presented here, you'll be equipped with the knowledge to recognize potential issues and seek appropriate treatment when necessary.
Read also:Top Patreon Alternatives For Creators Building A Thriving Community
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior
- Function of the Tibialis Anterior
- Common Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Diagnosing Tibialis Anterior Disorders
- Treatment Options for Tibialis Anterior Issues
- Preventing Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Exercises for Strengthening the Tibialis Anterior
- Stretching Techniques for the Tibialis Anterior
- Rehabilitation for Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior
The tibialis anterior is a long, thin muscle situated at the front of the lower leg, spanning from the lateral condyle of the tibia to the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones. Its primary role is to facilitate dorsiflexion of the foot, allowing the toes to point upward. This muscle is also responsible for inverting the foot, which helps maintain balance and stability during movement.
Key Features of Tibialis Anterior
- Origin: Lateral condyle of the tibia.
- Insertion: Medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones.
- Nerve Supply: Deep fibular nerve (L4-L5).
- Blood Supply: Anterior tibial artery.
Understanding the anatomical structure of the tibialis anterior is essential for diagnosing and treating related disorders. The muscle's location and function make it prone to strain and overuse, particularly in athletes or individuals who engage in repetitive foot movements.
Function of the Tibialis Anterior
The primary function of the tibialis anterior is dorsiflexion, which is the movement that allows the toes to point upward. This action is critical for walking, running, and other activities that require foot movement. Additionally, the tibialis anterior assists in foot inversion, which involves tilting the sole of the foot inward.
Role in Daily Activities
- Walking and running.
- Maintaining balance and posture.
- Supporting the arch of the foot.
- Assisting in climbing stairs and stepping over obstacles.
Without the proper functioning of the tibialis anterior, individuals may experience difficulty in performing these activities, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility.
Common Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Tibialis anterior injuries are prevalent, especially among athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive foot movements. Common conditions affecting this muscle include shin splints, tendonitis, and muscle strains. These injuries can result from overuse, improper footwear, or inadequate warm-up routines.
Symptoms of Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Pain in the front of the lower leg.
- Swelling and tenderness.
- Difficulty in dorsiflexion.
- Weakness in the foot and ankle.
Early recognition and treatment of these symptoms are crucial for preventing long-term damage and ensuring a swift recovery.
Read also:Unveiling The Glamour Of Dti Crystal Couture A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing Tibialis Anterior Disorders
Diagnosing tibialis anterior disorders typically involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests, and patient history reviews. Healthcare professionals may use X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasounds to assess the extent of the injury and determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Diagnostic Procedures
- Physical examination to evaluate pain and swelling.
- Imaging tests to identify structural damage.
- Electromyography (EMG) to assess nerve function.
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment strategy that addresses the specific needs of the patient.
Treatment Options for Tibialis Anterior Issues
Treatment for tibialis anterior disorders varies depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may require rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE method), while more severe injuries may necessitate physical therapy, medication, or even surgery.
Treatment Approaches
- RICE method for mild injuries.
- Physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility.
- Medication to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Surgical intervention for severe cases.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for determining the most appropriate treatment plan based on the individual's specific condition and needs.
Preventing Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Preventing tibialis anterior injuries involves adopting proper techniques during physical activities, wearing appropriate footwear, and maintaining muscle strength and flexibility. Regular exercise, stretching, and warm-up routines can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Preventive Measures
- Wear supportive footwear with adequate cushioning.
- Engage in regular stretching and strengthening exercises.
- Use proper techniques during physical activities.
- Gradually increase intensity and duration of workouts.
By following these preventive measures, individuals can minimize the likelihood of tibialis anterior injuries and maintain optimal muscle health.
Exercises for Strengthening the Tibialis Anterior
Strengthening the tibialis anterior is essential for improving muscle endurance and preventing injuries. Exercises targeting this muscle can enhance dorsiflexion and overall foot function. Below are some effective exercises for strengthening the tibialis anterior:
Recommended Exercises
- Toe raises: Stand on a step and raise your heels, keeping your toes on the edge.
- Resistance band dorsiflexion: Use a resistance band to pull your foot upward against resistance.
- Heel walks: Walk on your heels to engage the tibialis anterior muscle.
Incorporating these exercises into your routine can help build strength and resilience in the tibialis anterior.
Stretching Techniques for the Tibialis Anterior
Stretching the tibialis anterior can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury. Effective stretching techniques target the muscle fibers, promoting relaxation and reducing tension. Below are some recommended stretching techniques:
Effective Stretches
- Seated dorsiflexion stretch: Sit with your legs extended and pull your toes toward you.
- Standing calf stretch: Lean against a wall with one foot extended behind you, keeping your toes pointed forward.
- Towel stretch: Use a towel to gently pull your toes toward you while sitting.
Regular stretching can enhance the flexibility of the tibialis anterior, contributing to better overall foot function.
Rehabilitation for Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Rehabilitation is a critical component of recovering from tibialis anterior injuries. A structured rehabilitation program focuses on restoring strength, flexibility, and function to the affected muscle. Physical therapists often design personalized plans that address the specific needs of each patient.
Rehabilitation Components
- Progressive strengthening exercises.
- Gentle stretching routines.
- Balance and proprioception training.
- Gradual return to physical activities.
Following a rehabilitation program can significantly improve recovery outcomes and reduce the likelihood of re-injury.
Conclusion
The tibialis anterior is a vital muscle that plays a crucial role in foot movement, balance, and stability. Understanding its anatomy, function, and potential disorders can help in maintaining overall leg health and preventing injuries. By adopting preventive measures, engaging in regular exercises, and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary, individuals can ensure the optimal functioning of this essential muscle.
We encourage readers to share their experiences and insights in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more information on related topics. Together, let's promote awareness and understanding of the importance of muscle health and injury prevention.