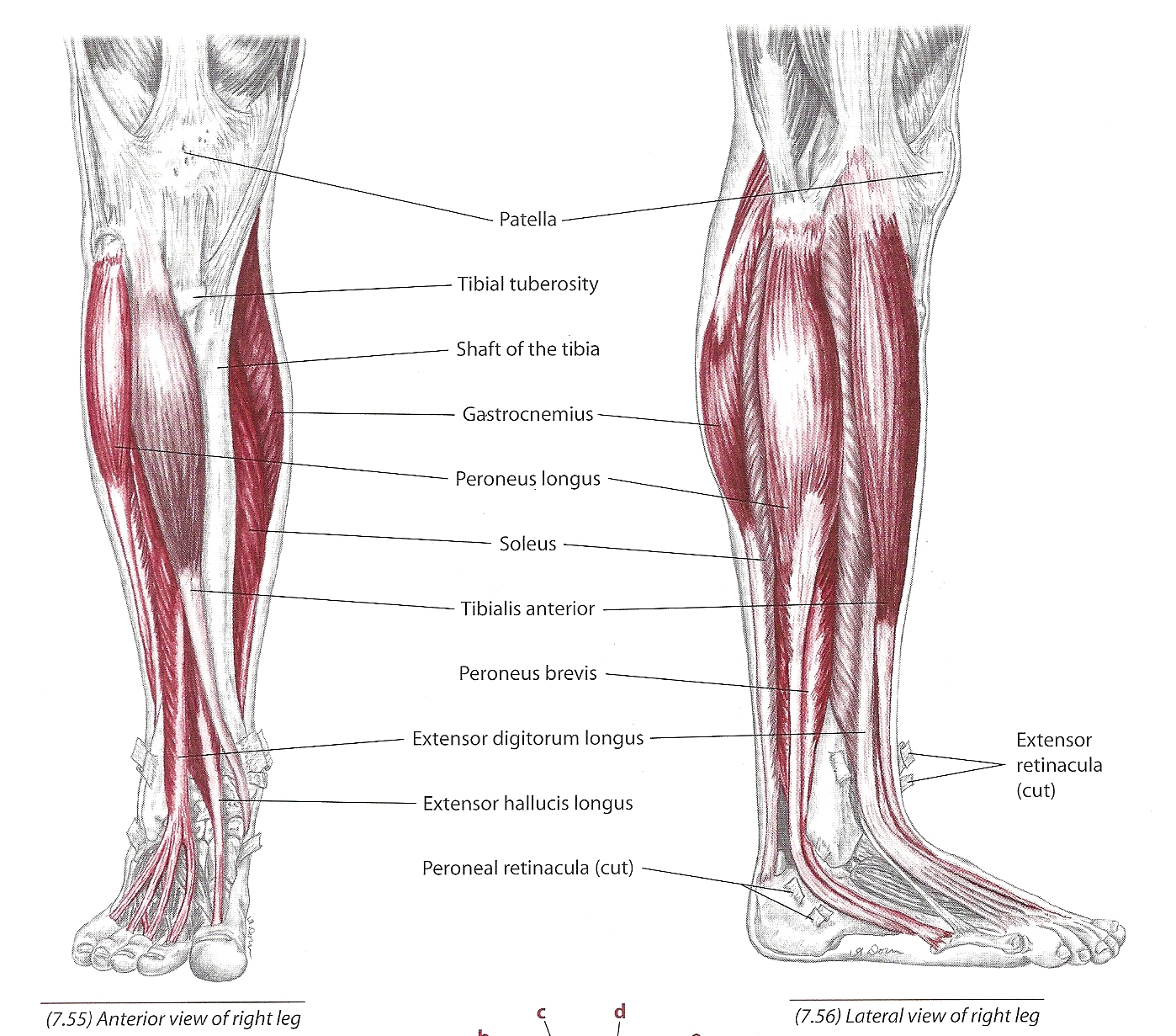
Tibialis muscle function plays a crucial role in the movement and stability of the foot and ankle. These muscles, including the tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior, are essential for walking, running, and maintaining balance. Understanding their roles can help you prevent injuries and improve overall leg health.
Whether you're an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or someone recovering from an injury, knowing how the tibialis muscles work can significantly enhance your daily activities. These muscles are often overlooked but are vital for proper foot alignment and movement.
In this article, we will explore the anatomy, functions, and importance of the tibialis muscles. Additionally, we will discuss common issues associated with these muscles, preventive measures, and exercises to strengthen them. Let's dive in!
Read also:Top Hotels Near Northbrook Court Mall Your Ultimate Guide
Table of Contents
- Tibialis Muscle Anatomy
- Functions of the Tibialis Muscles
- Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Tibialis Posterior Muscle
- Common Issues with Tibialis Muscles
- Preventing Tibialis Muscle Injuries
- Exercises to Strengthen Tibialis Muscles
- Rehabilitation for Tibialis Muscle Injuries
- Importance of Tibialis Muscle Health
- Conclusion
Tibialis Muscle Anatomy
The tibialis muscles are located in the lower leg and play a critical role in foot and ankle movement. There are two primary tibialis muscles: the tibialis anterior and the tibialis posterior. Both muscles are essential for maintaining stability and facilitating movement in the lower extremities.
Tibialis Anterior: This muscle is located on the front of the lower leg and is responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot. It originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones.
Tibialis Posterior: Situated deep in the posterior compartment of the leg, this muscle is vital for plantarflexion and inversion of the foot. It originates from the interosseous membrane and adjacent bones and inserts into multiple bones in the foot, including the navicular and cuneiform bones.
Functions of the Tibialis Muscles
The primary functions of the tibialis muscles include:
- Dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot
- Inversion of the foot
- Stabilizing the ankle joint
- Supporting the arch of the foot
Both muscles work together to ensure smooth and coordinated movement of the foot and ankle, which is essential for activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
Tibialis Anterior Muscle
Location and Structure
The tibialis anterior muscle is one of the largest muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg. It is a superficial muscle that runs along the front of the shin and is easily visible when the foot is dorsiflexed.
Read also:Mariska Hargitay Height Discover The Truth Behind Her Stature And Career
Key Features:
- Origin: Lateral condyle of the tibia
- Insertion: Medial cuneiform and base of the first metatarsal
- Function: Dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot
Role in Movement
The tibialis anterior muscle is primarily responsible for lifting the foot upward (dorsiflexion) and turning it inward (inversion). This action is crucial during the swing phase of walking, as it helps clear the foot from the ground.
Tibialis Posterior Muscle
Location and Structure
The tibialis posterior muscle is located deep in the posterior compartment of the leg. It is a strong and powerful muscle that plays a vital role in foot and ankle stability.
Key Features:
- Origin: Interosseous membrane, tibia, and fibula
- Insertion: Navicular, cuneiform, and other tarsal bones
- Function: Plantarflexion and inversion of the foot
Role in Movement
This muscle assists in plantarflexion and inversion of the foot, helping to stabilize the ankle joint and support the arch of the foot. It is particularly important during activities that require weight-bearing, such as walking and running.
Common Issues with Tibialis Muscles
Tibialis muscle injuries and conditions are relatively common, especially among athletes and individuals who engage in repetitive activities. Some of the most common issues include:
- Tibialis anterior tendinitis
- Tibialis posterior tendon dysfunction
- Shin splints
- Flat feet
These conditions can lead to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility, making it essential to address them promptly.
Preventing Tibialis Muscle Injuries
Preventing injuries to the tibialis muscles involves a combination of proper training techniques, stretching, and strengthening exercises. Here are some tips to help prevent tibialis muscle injuries:
- Wear appropriate footwear that provides adequate support
- Gradually increase the intensity and duration of physical activities
- Incorporate stretching and strengthening exercises into your routine
- Listen to your body and rest when necessary
By following these guidelines, you can reduce the risk of tibialis muscle injuries and maintain optimal leg health.
Exercises to Strengthen Tibialis Muscles
Strengthening the tibialis muscles can improve foot and ankle stability, enhance performance, and prevent injuries. Here are some effective exercises:
- Tibialis Anterior Strengthening: Resistance band dorsiflexion
- Tibialis Posterior Strengthening: Toe raises with resistance
- General Foot Strengthening: Towel curls and marble pick-ups
Performing these exercises regularly can significantly improve the strength and function of your tibialis muscles.
Rehabilitation for Tibialis Muscle Injuries
Rehabilitating tibialis muscle injuries involves a structured program of rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity. Key components of rehabilitation include:
- Rest and ice to reduce inflammation
- Stretching and strengthening exercises
- Gradual reintroduction of weight-bearing activities
Working with a qualified healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist, can help ensure a successful recovery.
Importance of Tibialis Muscle Health
Maintaining the health of your tibialis muscles is crucial for overall lower extremity function. Strong and flexible tibialis muscles contribute to:
- Improved balance and stability
- Reduced risk of injury
- Enhanced athletic performance
By prioritizing tibialis muscle health, you can enjoy a higher quality of life and better physical performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the tibialis muscles are essential for foot and ankle movement and stability. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and potential issues can help you maintain optimal leg health and prevent injuries. By incorporating preventive measures, strengthening exercises, and proper rehabilitation techniques, you can ensure that your tibialis muscles remain strong and functional.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from it and leave a comment below if you have any questions or insights. For more information on leg health and fitness, explore our other articles and resources.
Data Sources: