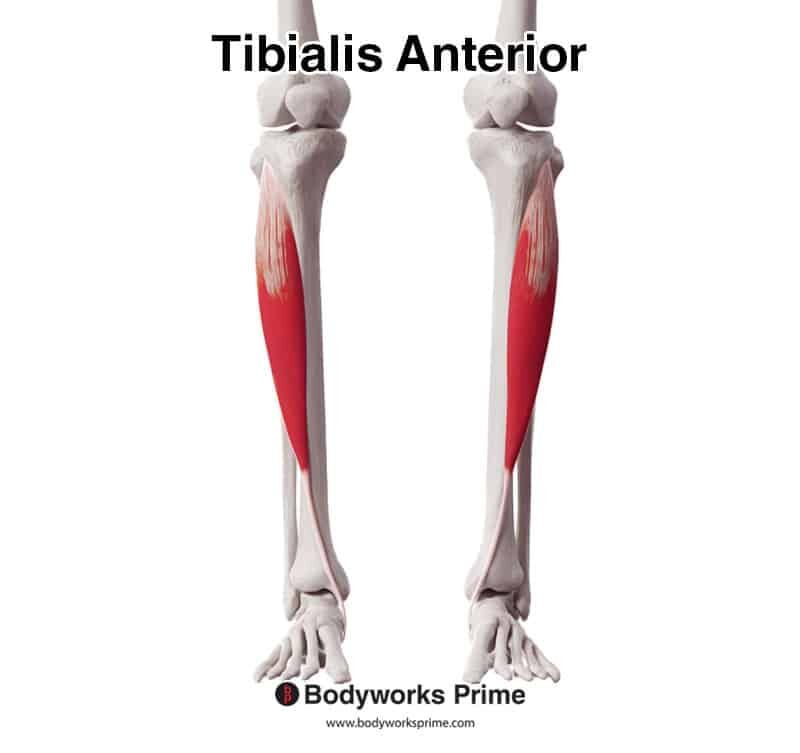
The anterior tibialis muscle plays a vital role in the movement and stability of the lower leg and foot. As one of the key muscles in the lower limb, it is responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot, making it essential for walking, running, and maintaining balance. Understanding its function is critical for anyone interested in anatomy, physical therapy, or sports science.
Injuries or dysfunction of the anterior tibialis can lead to significant mobility issues, including conditions like shin splints or compartment syndrome. This muscle is often overlooked, but its importance cannot be overstated. By delving into its anatomy, function, and potential problems, we can gain a deeper appreciation of its role in daily activities.
This article explores the anterior tibialis function in detail, covering its anatomy, importance in movement, common injuries, and treatment options. Whether you're a student of anatomy, a fitness enthusiast, or someone dealing with lower leg pain, this guide will provide valuable insights into this critical muscle.
Read also:Morristown Tn Dining A Comprehensive Guide To The Best Restaurants And Culinary Experiences
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Anterior Tibialis
- Primary Functions of Anterior Tibialis
- Role in Movement and Stability
- Common Injuries and Conditions
- Preventing Anterior Tibialis Injuries
- Treatment Options for Anterior Tibialis Issues
- Rehabilitation Exercises
- Variations in Anterior Tibialis Function
- Recent Research and Findings
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Anatomy of the Anterior Tibialis
Location and Structure
The anterior tibialis is a long, spindle-shaped muscle located on the front of the lower leg. It originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. This muscle is surrounded by a fibrous sheath and is innervated by the deep fibular nerve.
Key Characteristics
This muscle is part of the anterior compartment of the leg and works alongside other muscles like the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus. Its primary role is to facilitate movement at the ankle joint, making it indispensable for activities that involve the lower limbs.
Key Points:
- Originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia.
- Inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones.
- Innervated by the deep fibular nerve.
Primary Functions of Anterior Tibialis
Dorsiflexion of the Foot
The anterior tibialis is primarily responsible for dorsiflexion, the upward movement of the foot at the ankle joint. This action is crucial for walking, as it allows the foot to lift off the ground during the swing phase of gait.
Inversion of the Foot
In addition to dorsiflexion, the anterior tibialis also assists in the inversion of the foot, which involves tilting the sole inward. This contributes to the stability of the foot and ankle during movement.
Role in Movement and Stability
The anterior tibialis function extends beyond basic movement. It plays a significant role in maintaining stability during dynamic activities such as running, jumping, and climbing stairs. Its ability to control the rate of plantarflexion (downward movement of the foot) is essential for shock absorption and smooth transitions between steps.
Read also:Top Hotels Near Northbrook Court Mall Your Ultimate Guide
Key Movements Supported:
- Walking and running
- Climbing stairs
- Jumping and landing
Common Injuries and Conditions
Shin Splints
One of the most common issues related to the anterior tibialis is shin splints, a condition characterized by pain along the shinbone. This often occurs due to overuse or improper footwear, leading to inflammation of the muscle and surrounding tissues.
Compartment Syndrome
Another potential problem is anterior compartment syndrome, which can be acute or chronic. This condition arises when pressure within the muscle compartment increases to dangerous levels, potentially leading to permanent damage if not treated promptly.
Preventing Anterior Tibialis Injuries
Preventing injuries to the anterior tibialis involves a combination of proper technique, adequate rest, and targeted exercises. Wearing appropriate footwear, gradually increasing activity levels, and incorporating stretching and strengthening routines can significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Preventive Measures:
- Wear supportive footwear
- Increase activity levels gradually
- Stretch and strengthen the muscle regularly
Treatment Options for Anterior Tibialis Issues
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is often recommended for individuals experiencing anterior tibialis dysfunction. Techniques such as manual therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation can help reduce pain and improve muscle function.
Medication and Rest
In some cases, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications and rest may be sufficient to alleviate symptoms. However, chronic conditions may require more advanced interventions, such as corticosteroid injections or surgery.
Rehabilitation Exercises
Rehabilitation exercises are crucial for restoring strength and function to the anterior tibialis. These exercises focus on improving flexibility, endurance, and coordination of the muscle.
Sample Exercises:
- Towel dorsiflexion
- Resistance band exercises
- Calf raises with toe lift
Variations in Anterior Tibialis Function
While the primary functions of the anterior tibialis are consistent, variations in anatomy and biomechanics can influence its performance. Factors such as muscle length, tendon attachment, and individual gait patterns can affect how the muscle operates in different individuals.
Recent Research and Findings
Recent studies have shed light on the importance of the anterior tibialis in athletic performance and injury prevention. Research has highlighted the role of neuromuscular training in enhancing muscle function and reducing the incidence of related injuries.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Sports Sciences found that targeted strengthening exercises significantly improved dorsiflexion strength in athletes, reducing the risk of shin splints and other lower leg injuries.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The anterior tibialis function is critical for movement, stability, and overall lower limb health. By understanding its anatomy, role in movement, and potential issues, we can take proactive steps to prevent injuries and maintain optimal muscle function.
We encourage readers to explore further resources, consult with healthcare professionals, and implement the preventive and rehabilitative strategies discussed in this article. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to check out our other articles for more insights into anatomy and fitness.
References:
- Journal of Sports Sciences
- Mayo Clinic
- WebMD