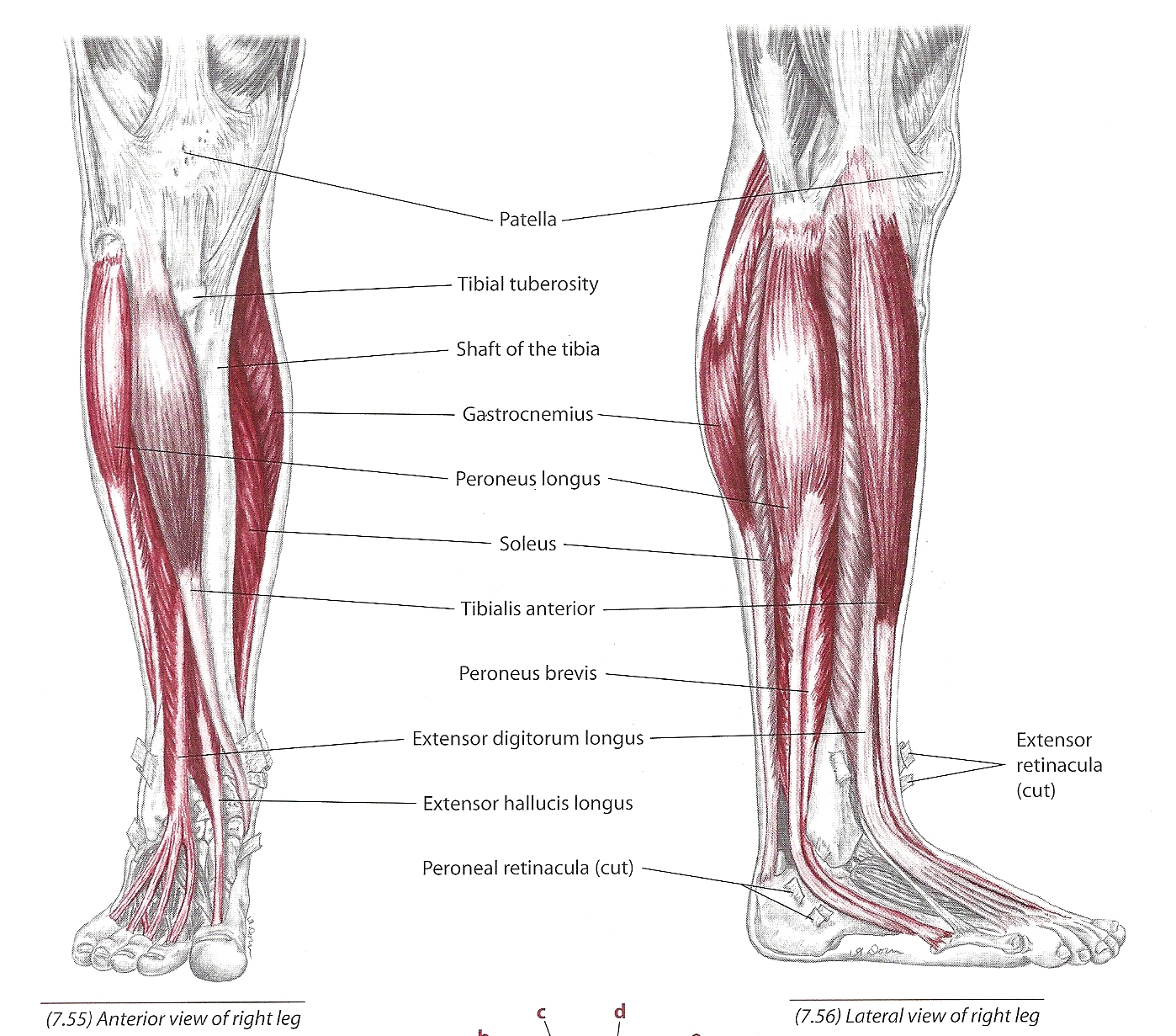
The tibialis muscle plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, stability, and mobility in our daily lives. Whether you're walking, running, or simply standing, the tibialis muscle group is actively involved. This muscle group consists of two primary muscles: tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior. Understanding their functions and significance is essential for anyone looking to improve their physical health and prevent injuries.
The tibialis muscle group is often overlooked in fitness routines and rehabilitation programs, yet it is one of the most important muscle groups in the lower body. When functioning properly, these muscles help stabilize the ankle joint, support the arch of the foot, and facilitate smooth movement. However, issues such as tibialis anterior tendonitis or tibialis posterior dysfunction can significantly impact mobility and quality of life.
In this article, we will delve into the anatomy, function, common conditions, and exercises associated with the tibialis muscle. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how these muscles work and how to maintain their health. Whether you're a fitness enthusiast, physical therapist, or someone dealing with foot or ankle issues, this article will provide valuable insights into the tibialis muscle.
Read also:Unveiling The Glamour Of Dti Crystal Couture A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents:
- Anatomy of the Tibialis Muscle
- Function of the Tibialis Muscle
- Common Conditions Affecting the Tibialis Muscle
- Diagnosis of Tibialis Muscle Issues
- Treatment Options for Tibialis Muscle Problems
- Exercises to Strengthen the Tibialis Muscle
- Prevention Strategies
- Nutrition and Tibialis Muscle Health
- Professional Care and Rehabilitation
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Tibialis Muscle
The tibialis muscle group is located in the lower leg and plays a vital role in foot and ankle movement. It consists of two primary muscles:
Tibialis Anterior
The tibialis anterior is the larger and more prominent muscle in the group. It originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones. This muscle is responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot, making it essential for walking, running, and maintaining balance.
Tibialis Posterior
The tibialis posterior is a deep muscle located behind the tibia. It originates from the interosseous membrane and inserts into various bones of the foot, including the navicular and cuneiform bones. This muscle is primarily responsible for plantarflexion and inversion of the foot, as well as supporting the medial arch of the foot.
Function of the Tibialis Muscle
The tibialis muscle group performs several critical functions that contribute to overall lower body mobility and stability.
- Dorsiflexion: The tibialis anterior helps lift the foot upward, which is essential for activities such as walking and climbing stairs.
- Inversion: Both the tibialis anterior and posterior assist in turning the sole of the foot inward, providing stability during movement.
- Arch Support: The tibialis posterior plays a key role in supporting the medial arch of the foot, preventing conditions like flat feet.
- Balance: These muscles work together to maintain balance and prevent falls, especially on uneven surfaces.
Common Conditions Affecting the Tibialis Muscle
Several conditions can affect the tibialis muscle group, leading to pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility.
Read also:Kylie Jenners Dad The Story Behind The Fame
Tibialis Anterior Tendonitis
Tendonitis in the tibialis anterior is often caused by overuse or repetitive strain. Symptoms include pain along the front of the shin, swelling, and difficulty with dorsiflexion.
Tibialis Posterior Dysfunction
Tibialis posterior dysfunction, also known as posterior tibial tendon dysfunction (PTTD), is a common cause of flat feet. This condition results in pain along the inner side of the ankle and difficulty with inversion.
Shin Splints
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, can affect both the tibialis anterior and posterior muscles. This condition is characterized by pain along the shinbone and is often seen in runners and athletes.
Diagnosis of Tibialis Muscle Issues
Diagnosing issues with the tibialis muscle typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and patient history.
Physical Examination
A healthcare professional will assess the range of motion, strength, and flexibility of the foot and ankle. They may also check for tenderness, swelling, or deformities.
Imaging Tests
Ultrasound and MRI scans can provide detailed images of the tibialis muscles and tendons, helping to identify tears, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
Treatment Options for Tibialis Muscle Problems
Treatment for tibialis muscle issues depends on the severity and type of condition. Common approaches include:
Rest and Activity Modification
Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pain is often the first step in treatment.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the tibialis muscles, improve flexibility, and restore function.
Medications
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
Exercises to Strengthen the Tibialis Muscle
Strengthening the tibialis muscle group can help prevent injuries and improve overall foot and ankle health. Here are some effective exercises:
- Toe Raises: Stand with your feet flat on the ground and slowly raise your heels, lifting onto your toes. Hold for a few seconds and lower back down.
- Resisted Inversion: Use a resistance band to perform foot inversion exercises, targeting the tibialis posterior.
- Calf Raises: Perform calf raises to strengthen the tibialis anterior and improve dorsiflexion.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing tibialis muscle issues involves adopting healthy habits and practices:
- Proper Footwear: Wear shoes that provide adequate support and cushioning.
- Stretching: Incorporate regular stretching exercises for the lower leg muscles.
- Gradual Progression: Increase activity levels gradually to avoid overuse injuries.
Nutrition and Tibialis Muscle Health
Nutrition plays a vital role in muscle health. Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, such as calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium, can support the tibialis muscles and promote healing.
Professional Care and Rehabilitation
In cases of severe tibialis muscle issues, professional care from a physical therapist or orthopedic specialist may be necessary. Rehabilitation programs can include manual therapy, custom orthotics, and advanced treatment techniques.
Conclusion
The tibialis muscle group is an essential component of lower body mobility and stability. Understanding its anatomy, function, and potential issues can help individuals take proactive steps to maintain their health. By incorporating strengthening exercises, adopting prevention strategies, and seeking professional care when needed, you can ensure the longevity and functionality of your tibialis muscles.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from learning about the tibialis muscle. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. Additionally, explore our other articles for more insights into health and fitness topics.
Data and references for this article are sourced from reputable organizations such as the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (AAOS) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH).