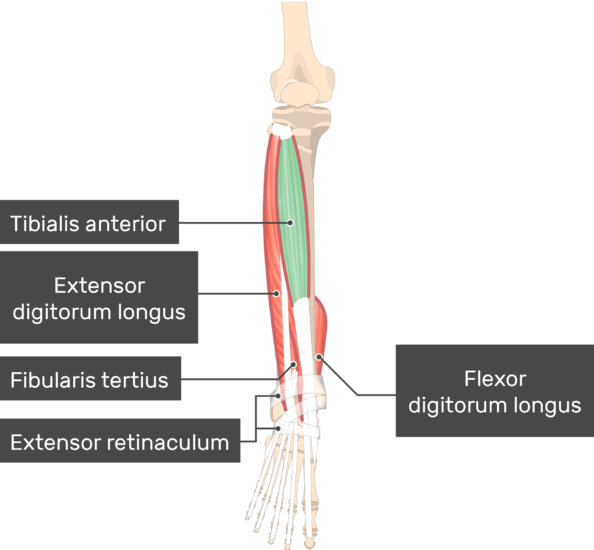
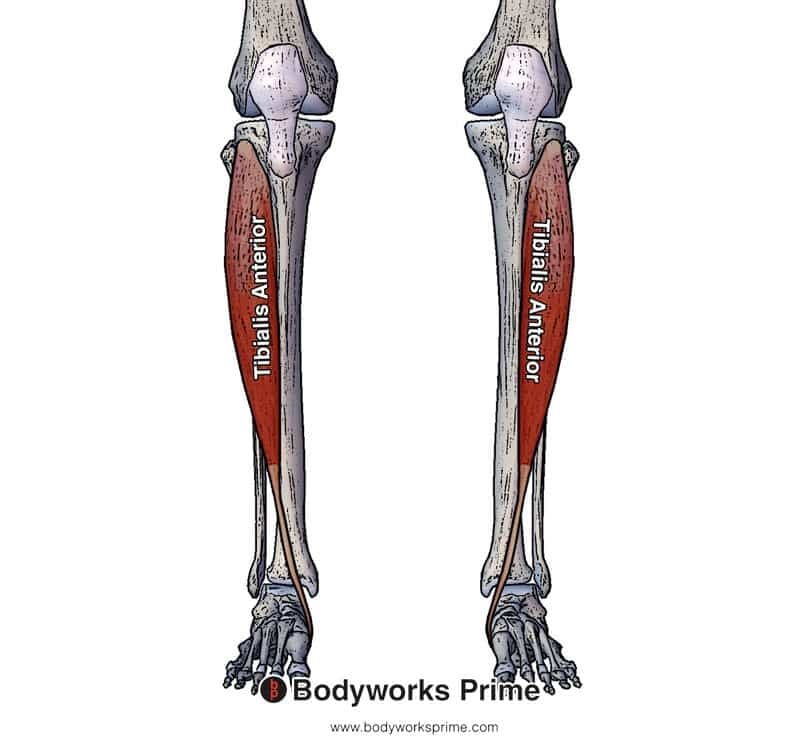
The tibialis anterior muscle plays a crucial role in the movement and stability of the lower leg and foot. This muscle is one of the key components of the anterior compartment of the leg and is responsible for several essential functions. Understanding its action can provide valuable insights into human anatomy and movement mechanics, particularly for athletes, healthcare professionals, and fitness enthusiasts.
Located on the front of the lower leg, the tibialis anterior is a long, spindle-shaped muscle that spans from the upper part of the tibia to the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. Its primary function revolves around dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot, making it indispensable for activities such as walking, running, and maintaining balance.
As we delve deeper into this article, we will explore the anatomy, actions, and importance of the tibialis anterior muscle. Additionally, we will discuss common injuries associated with this muscle and provide practical tips for strengthening and rehabilitation. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of the tibialis anterior and its role in human movement.
Read also:Morristown Tn Dining A Comprehensive Guide To The Best Restaurants And Culinary Experiences
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior
- Primary Action of the Tibialis Anterior
- Secondary Actions of the Muscle
- Common Injuries and Conditions
- Prevention and Management of Tibialis Anterior Injuries
- Strengthening Exercises
- Rehabilitation Techniques
- Importance in Daily Activities
- Role in Athletic Performance
- Conclusion
Anatomy of the Tibialis Anterior
The tibialis anterior is a prominent muscle located in the anterior compartment of the leg. It originates from the lateral condyle and upper two-thirds of the lateral surface of the tibia. From there, it runs down the leg, crossing the ankle joint and inserting into the medial cuneiform and the base of the first metatarsal bone.
Structure and Location
This muscle is covered by the deep fascia of the leg and is separated from the fibula by the interosseous membrane. Its location makes it a superficial muscle, easily palpable just beneath the skin on the front of the shin.
Key anatomical features of the tibialis anterior include:
- Origin: Lateral condyle and upper two-thirds of the tibia
- Insertion: Medial cuneiform and base of the first metatarsal
- Function: Dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot
Primary Action of the Tibialis Anterior
The primary action of the tibialis anterior is dorsiflexion of the foot at the ankle joint. Dorsiflexion refers to the movement that brings the toes closer to the shin, effectively lifting the foot upward. This action is critical for various daily activities, including walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Role in Gait
During the gait cycle, the tibialis anterior plays a vital role in the swing phase. It helps to clear the foot from the ground, ensuring a smooth transition between steps. Without adequate dorsiflexion, individuals may experience difficulty in walking or develop compensatory movements that can lead to further injuries.
Secondary Actions of the Muscle
In addition to dorsiflexion, the tibialis anterior also assists in foot inversion. Inversion involves tilting the sole of the foot medially, which is important for maintaining balance and stability, especially on uneven surfaces.
Read also:Anna Smrek Height Unveiling The Truth About This Iconic Model
Balance and Stability
By stabilizing the ankle joint during movement, the tibialis anterior helps prevent excessive pronation or supination of the foot. This contributes to overall joint health and reduces the risk of ankle sprains and other related injuries.
Common Injuries and Conditions
Despite its strength and functionality, the tibialis anterior is susceptible to various injuries. Shin splints, tendonitis, and muscle strains are among the most common conditions associated with this muscle.
Shin Splints
Shin splints, or medial tibial stress syndrome, occur when the tibialis anterior becomes overworked or inflamed. This condition is often seen in runners and athletes who engage in repetitive high-impact activities.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis of the tibialis anterior involves inflammation of the tendon, leading to pain and discomfort along the front of the shin. This condition can be exacerbated by overuse or improper footwear.
Prevention and Management of Tibialis Anterior Injuries
Preventing injuries to the tibialis anterior involves a combination of proper training techniques, appropriate footwear, and regular stretching and strengthening exercises.
Stretching Exercises
Incorporating targeted stretches for the tibialis anterior can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injury. Examples include:
- Seated shin stretch
- Wall dorsiflexion stretch
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening the tibialis anterior is essential for enhancing its functionality and resilience. Exercises such as resistance band dorsiflexion and toe raises can be highly effective.
Strengthening Exercises
Engaging in regular strengthening exercises can significantly improve the strength and endurance of the tibialis anterior. These exercises are particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals recovering from injuries.
Resistance Band Dorsiflexion
This exercise involves attaching a resistance band to a stationary object and looping it around the foot. By pulling the toes upward against the resistance, the tibialis anterior is effectively targeted and strengthened.
Rehabilitation Techniques
Rehabilitating an injured tibialis anterior requires a structured approach that includes rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to activity. Techniques such as ultrasound therapy, massage, and manual manipulation can aid in the recovery process.
Physical Therapy
A physical therapist can design a personalized rehabilitation program tailored to the specific needs of the individual. This may include exercises, modalities, and education on injury prevention strategies.
Importance in Daily Activities
The tibialis anterior is vital for performing daily activities that involve lower extremity movement. Its role in dorsiflexion and inversion ensures that individuals can navigate their environment with ease and confidence.
Walking and Running
Whether walking on flat surfaces or running on uneven terrain, the tibialis anterior works tirelessly to maintain proper foot positioning and joint stability. This muscle's functionality directly impacts the efficiency and safety of these activities.
Role in Athletic Performance
For athletes, the tibialis anterior is a key player in optimizing performance. Its ability to facilitate rapid and controlled movements is crucial for sports that require agility, speed, and precision.
Sport-Specific Training
Athletes can enhance their tibialis anterior strength through sport-specific training programs. These programs often incorporate plyometric exercises, resistance training, and dynamic stretching to improve muscle performance.
Conclusion
In summary, the tibialis anterior is a critical muscle responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot. Its role in daily activities and athletic performance cannot be overstated. By understanding its anatomy, actions, and potential injuries, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain its health and functionality.
We encourage readers to explore the provided exercises and rehabilitation techniques to enhance their tibialis anterior strength and prevent future injuries. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to check out other informative articles on our website!