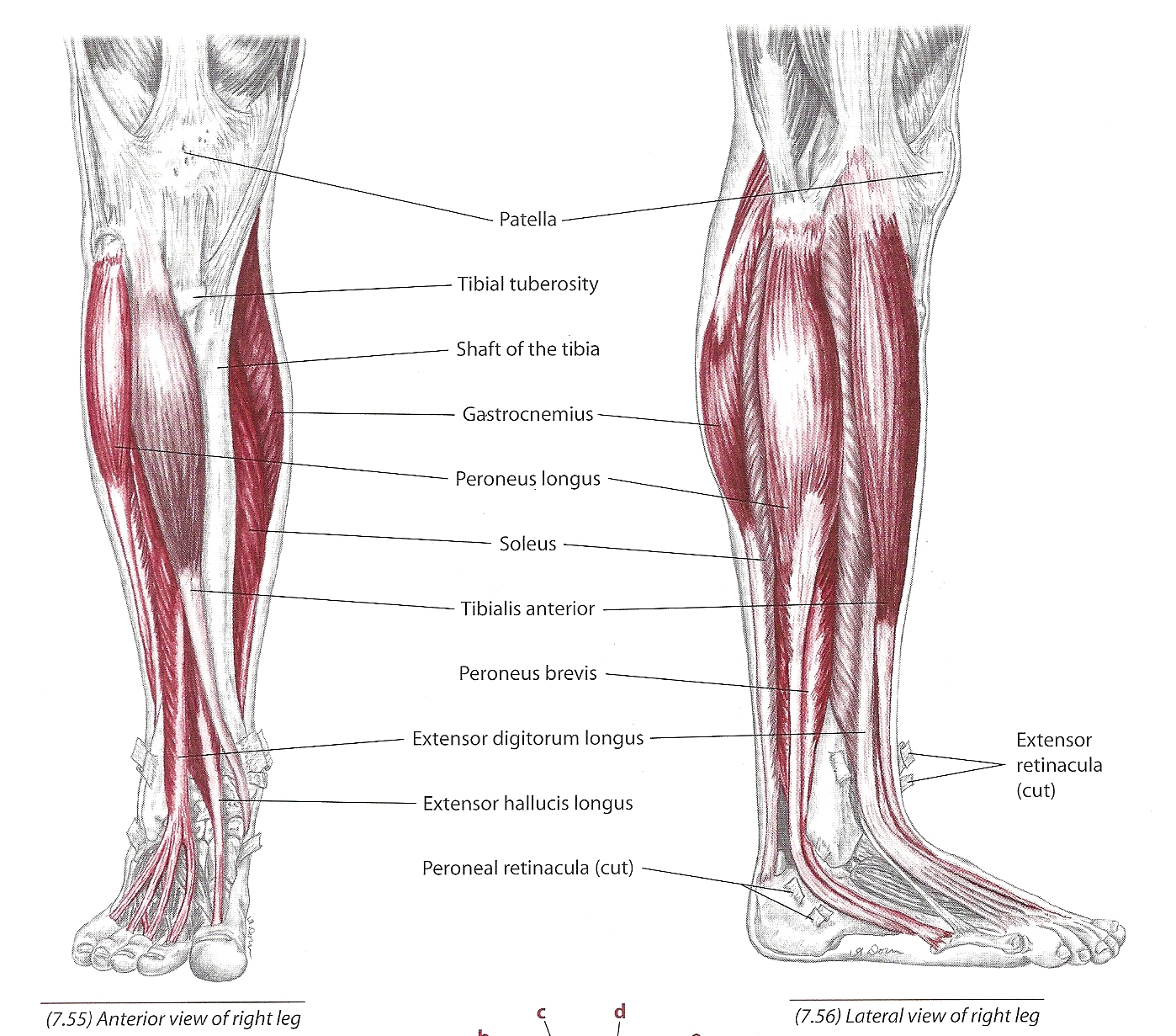
The tibialis anterior muscle plays a crucial role in our body's movement and stability. Whether you're walking, running, or simply standing, this muscle is actively involved. Understanding its function can help in diagnosing and treating various musculoskeletal conditions.
As we delve into the world of anatomy, the tibialis anterior muscle is one of the essential muscles located in the lower leg. It is not only vital for movement but also for maintaining balance. This article will explore its functions, anatomy, and its importance in our daily activities.
Whether you're a healthcare professional, a fitness enthusiast, or someone interested in human anatomy, this guide will provide you with an in-depth understanding of the tibialis anterior muscle and its role in our body. Let's dive in!
Read also:Monsters Inc Salamander Unveiling The Fascinating World Of Amphibian Stars
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Function of Tibialis Anterior Muscle
- Location and Structure
- Role in Movement
- Common Injuries and Conditions
- Exercises to Strengthen the Muscle
- Rehabilitation Techniques
- Importance in Daily Life
- Diagnosis and Treatment
- Conclusion
Anatomy of Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The tibialis anterior muscle is a key component of the anterior compartment of the lower leg. It originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and the first metatarsal bone. This muscle is primarily responsible for dorsiflexion and inversion of the foot.
This muscle is surrounded by the deep fascia of the leg and is innervated by the deep fibular nerve. Blood supply to the tibialis anterior muscle comes from the anterior tibial artery, which ensures its continuous function and repair.
Key Features of the Muscle
The tibialis anterior muscle is characterized by its long tendinous origin and insertion, which allows for efficient movement and force generation. It plays a crucial role in stabilizing the ankle joint during various activities.
Function of Tibialis Anterior Muscle
The primary function of the tibialis anterior muscle is to facilitate dorsiflexion of the foot. This movement is essential for activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs. Additionally, the muscle aids in the inversion of the foot, which helps in maintaining balance and stability.
Its ability to control the descent of the foot during the gait cycle is vital for preventing injuries and ensuring smooth movement. The tibialis anterior muscle works in coordination with other muscles in the lower leg to achieve optimal functionality.
Variations in Function
- Assists in stabilizing the ankle joint during movement.
- Contributes to the proper alignment of the foot.
- Helps in absorbing shock during high-impact activities.
Location and Structure
Located in the anterior compartment of the lower leg, the tibialis anterior muscle spans from the upper two-thirds of the lateral surface of the tibia to the medial cuneiform and the base of the first metatarsal bone. Its structure consists of long, slender muscle fibers that allow for efficient contraction and relaxation.
Read also:Anna Smrek Height Unveiling The Truth About This Iconic Model
The muscle is covered by the deep fascia of the leg, which provides additional support and protection. Its tendinous insertion ensures strong attachment to the bones, enhancing its ability to generate force.
Role in Movement
The tibialis anterior muscle is instrumental in various movements of the foot and ankle. Its primary role in dorsiflexion and inversion makes it indispensable for activities that require foot and ankle movement.
During the gait cycle, the muscle helps in controlling the foot's movement, ensuring a smooth transition from heel strike to toe-off. This coordinated movement is crucial for maintaining balance and preventing injuries.
Key Movements Supported
- Dorsiflexion of the foot.
- Inversion of the foot.
- Stabilization of the ankle joint.
Common Injuries and Conditions
Like any other muscle, the tibialis anterior muscle is susceptible to injuries and conditions that can affect its function. Common issues include shin splints, tendonitis, and compartment syndrome.
Shin splints, characterized by pain along the tibia, often occur due to overuse or improper training techniques. Tendonitis, on the other hand, involves inflammation of the tendon, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
Preventing Injuries
- Proper warm-up and stretching before exercise.
- Gradual increase in training intensity.
- Wearing appropriate footwear.
Exercises to Strengthen the Muscle
Strengthening the tibialis anterior muscle is essential for maintaining its function and preventing injuries. Several exercises can be performed to enhance its strength and flexibility.
Toe raises, resistance band exercises, and ankle circles are effective in targeting this muscle. These exercises not only improve muscle strength but also enhance overall foot and ankle stability.
Recommended Exercises
- Toe Raises: Stand with feet flat on the ground and slowly lift your toes off the floor.
- Resistance Band Exercises: Use a resistance band to add tension during dorsiflexion movements.
- Ankle Circles: Rotate your ankle in circular motions to improve flexibility.
Rehabilitation Techniques
In cases of injury or surgery involving the tibialis anterior muscle, rehabilitation is crucial for restoring its function. Physical therapy programs often include exercises that focus on strengthening, flexibility, and proprioception.
Manual therapy, ultrasound treatment, and electrical stimulation are some of the techniques used to aid recovery. These methods help in reducing pain, improving blood flow, and enhancing muscle function.
Rehabilitation Goals
- Restoring muscle strength and flexibility.
- Improving balance and coordination.
- Preventing future injuries.
Importance in Daily Life
The tibialis anterior muscle plays a vital role in our daily activities, from walking to more complex movements. Its ability to control foot movement and maintain balance is essential for performing tasks efficiently and safely.
In addition to its functional importance, the muscle also contributes to the aesthetic appearance of the lower leg. A well-developed tibialis anterior muscle can enhance the overall look of the leg, making it a focus in fitness and bodybuilding circles.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing issues related to the tibialis anterior muscle involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and clinical history. Physicians often use MRI or ultrasound to assess the muscle's condition and identify any abnormalities.
Treatment options range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to more invasive procedures such as surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the patient's overall health.
Treatment Options
- Rest and ice application.
- Physical therapy and exercises.
- Surgical intervention in severe cases.
Conclusion
The tibialis anterior muscle is a critical component of the lower leg, playing a vital role in movement, stability, and balance. Understanding its anatomy, function, and importance can help in diagnosing and treating various musculoskeletal conditions.
We encourage you to explore the exercises and rehabilitation techniques discussed in this article to maintain the health and functionality of your tibialis anterior muscle. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to share them below. Additionally, consider exploring other articles on our site for more insights into human anatomy and fitness.
References:
- Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice
- Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy
- Mayo Clinic: Tibialis Anterior Injuries