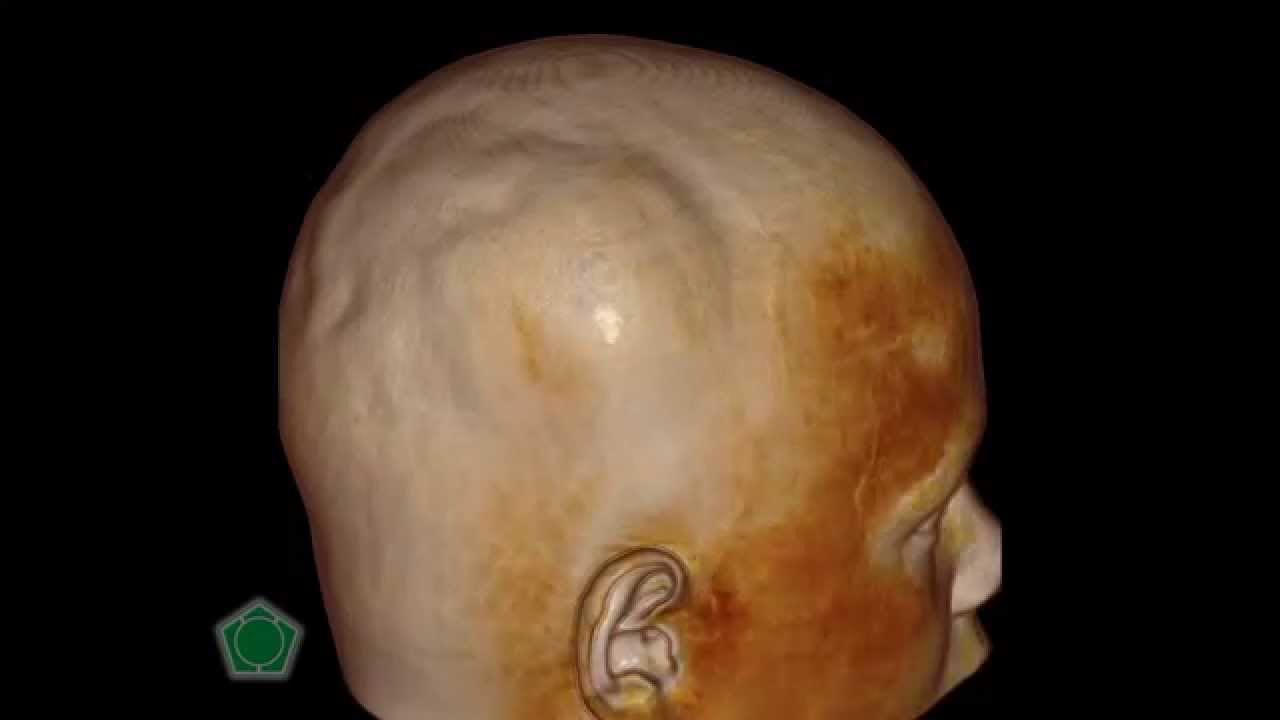
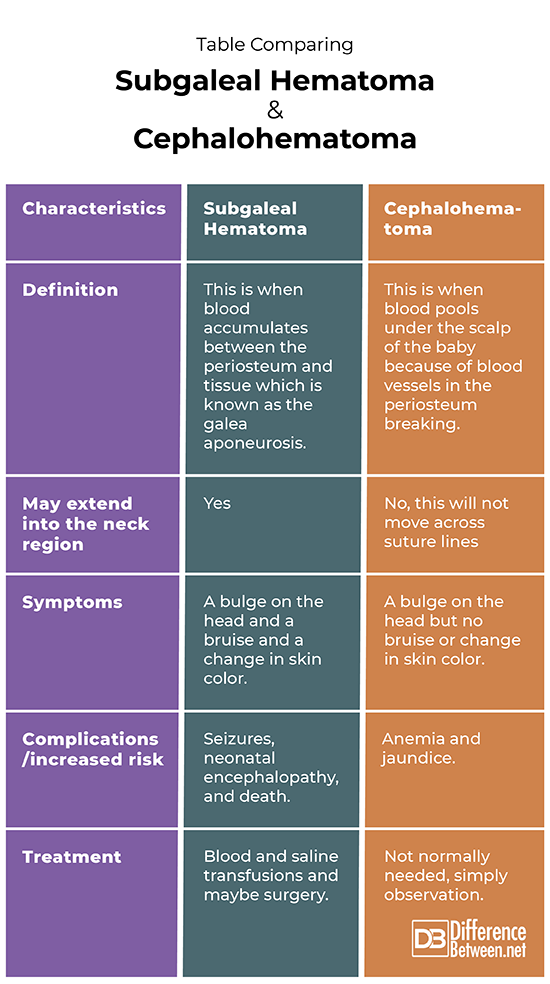
Subgaleal hematoma is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood accumulates in the subgaleal space, which is located between the periosteum and the galea aponeurotica of the scalp. This condition is particularly concerning in newborns and infants, as it can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for subgaleal hematoma, ensuring you are well-informed about this critical medical issue.
Subgaleal hematoma is not just a medical term; it represents a life-threatening situation that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the condition in detail can help parents and caregivers recognize the signs early and seek appropriate medical care.
This article aims to provide comprehensive information about subgaleal hematoma, including its risk factors, how it is diagnosed, and the available treatment options. We will also explore preventive measures to help reduce the likelihood of its occurrence.
Read also:Brown Blood Before Period Understanding The Causes And What It Means For Your Health
What is Subgaleal Hematoma?
Subgaleal hematoma refers to the accumulation of blood in the subgaleal space, a potential space between the periosteum of the skull and the galea aponeurotica. This space is relatively large, allowing for significant blood accumulation, which can lead to hypovolemic shock in infants. The condition is most commonly observed in newborns, often as a result of trauma during delivery.
Key Characteristics of Subgaleal Hematoma
- Occurs in the subgaleal space of the scalp.
- Can result in substantial blood loss, leading to shock.
- Primarily affects newborns and infants.
Causes of Subgaleal Hematoma
Subgaleal hematoma is typically caused by trauma to the scalp, particularly during childbirth. The use of vacuum extraction or forceps during delivery can increase the risk of this condition. Additionally, difficult or prolonged labor may contribute to the development of subgaleal hematoma.
Common Risk Factors
- Use of vacuum extraction during delivery.
- Use of forceps during childbirth.
- Difficult or prolonged labor.
- Instrument-assisted deliveries.
Symptoms of Subgaleal Hematoma
The symptoms of subgaleal hematoma can vary depending on the severity of the condition. However, some common signs include swelling of the scalp, discoloration, and a noticeable lump. Infants may also exhibit signs of distress, such as irritability, poor feeding, and lethargy.
Signs to Watch For
- Swelling or bulging on the scalp.
- Discoloration of the skin.
- Irritability or excessive crying.
- Poor feeding and lethargy.
Diagnosis of Subgaleal Hematoma
Diagnosing subgaleal hematoma involves a thorough physical examination and the use of imaging techniques such as ultrasound or CT scans. These tools help healthcare providers assess the extent of the hematoma and determine the appropriate course of action.
Diagnostic Tools
- Physical examination of the scalp.
- Ultrasound imaging.
- CT scans for detailed visualization.
Treatment Options for Subgaleal Hematoma
The treatment of subgaleal hematoma focuses on stabilizing the infant and managing blood loss. In severe cases, blood transfusions may be necessary to address hypovolemic shock. Additionally, close monitoring and supportive care are essential to ensure the infant's recovery.
Steps in Treatment
- Stabilization of the infant's condition.
- Blood transfusions if significant blood loss occurs.
- Close monitoring and supportive care.
Prevention of Subgaleal Hematoma
Preventing subgaleal hematoma involves minimizing the risk factors associated with its development. This includes careful monitoring during labor and delivery, as well as the judicious use of delivery instruments. Educating healthcare providers about the risks and proper techniques can also play a crucial role in prevention.
Read also:Unveiling The Glamour Of Dti Crystal Couture A Comprehensive Guide
Preventive Measures
- Minimize the use of delivery instruments unless necessary.
- Ensure proper training for healthcare providers.
- Monitor labor and delivery closely for signs of distress.
Complications Associated with Subgaleal Hematoma
Subgaleal hematoma can lead to severe complications if not treated promptly. Hypovolemic shock is a significant concern, as it can result in organ failure and even death. Early recognition and intervention are critical to preventing these complications.
Potential Complications
- Hypovolemic shock.
- Organ failure.
- Long-term developmental issues.
Recovery and Follow-Up Care
Recovery from subgaleal hematoma requires close follow-up care to ensure the infant's health and well-being. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the infant's progress and address any lingering issues.
Importance of Follow-Up
- Regular check-ups to monitor recovery.
- Addressing any developmental concerns.
- Providing support for parents and caregivers.
Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
While subgaleal hematoma is most commonly associated with infants, it can also occur in adults, typically as a result of trauma or surgery. The symptoms and treatment options are similar, but the context and risk factors may differ.
Differences in Adults
- Often caused by trauma or surgery.
- Similar symptoms but different risk factors.
- Management and treatment are similar to infants.
Expert Insights and Research
Research into subgaleal hematoma continues to evolve, with studies focusing on improving diagnostic techniques and treatment protocols. Experts in the field emphasize the importance of early recognition and intervention to improve outcomes for affected infants.
Key Research Findings
- Improved imaging techniques for diagnosis.
- Advancements in treatment protocols.
- Focus on preventive measures and education.
Conclusion
In conclusion, subgaleal hematoma is a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can help parents and caregivers recognize the signs early and seek appropriate medical care. By following preventive measures and ensuring close follow-up care, the risks associated with this condition can be minimized.
We encourage readers to share this article with others who may benefit from the information. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave them below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site for more insightful content on various health topics.
Table of Contents
- What is Subgaleal Hematoma?
- Causes of Subgaleal Hematoma
- Symptoms of Subgaleal Hematoma
- Diagnosis of Subgaleal Hematoma
- Treatment Options for Subgaleal Hematoma
- Prevention of Subgaleal Hematoma
- Complications Associated with Subgaleal Hematoma
- Recovery and Follow-Up Care
- Subgaleal Hematoma in Adults
- Expert Insights and Research